- 1. Overview
- 2. Common u-boot
- 3. Common Linux
- 4. core-1 Linux OS 启动
- 5. core0 和 core1 通信
- 6. hwwd/reset/watchdog driver
1. Overview
项目需要在一个 4 核的 SoC(System on a Chip) 处理器上面运行 Linux 和 VxWorks 两个操作系统: core-0/2/3 运行 Linux OS, core-1 运行 VxWorks OS; core-0/2/3 Linux OS 由中国团队开发,core-1 VxWorks OS 由国外团队开发。先启动 Linux OS, 由 Linux OS 启动 VxWorks OS。因为 VxWorks OS 开发进展较慢,我们决定现在 core-1 启动另外一个 Linux OS 来 derisk, 提前验证 Linux OS AMP 的启动方案, 验证 Linux Kernel remoteproc driver, RPMsg/Virtio driver 等。后来这套运行两个 Linux OS 的 AMP 方案还差点用到产品上面,这是后话。下图是系统框图:
2. Common u-boot
core0 和 core1 共用同一个 u-boot,在运行时识别 coreid 来选择执行相应的代码。这是这个方案的重点和难点,涉及对 u-boot 的深度修改。
- 在 uboot-core0/include/configs/octeon_lmnta.h 中定义板级 config 选项
#defind CONFIG_SUPPORT_CORE1_BOOT 1, 用来处理公共代码。 - 在 struct bd_info(arch/mips/include/asm/u-boot.h)增加两个新成员:coreid 和 sdram_base(ram基地址)。
- 增加 core-1.dts, 只包含 core-1 管理的硬件配置:uart0,中断控制器等。
- 从 start.S 开始,一共使用了 10 个 changesets 修改 u-boot, 主要是使用 coreid 在运行时区分 core0 或者 core1 来运行,选择执行相应的硬件资源,如 uart,ram,Exception Base 等。
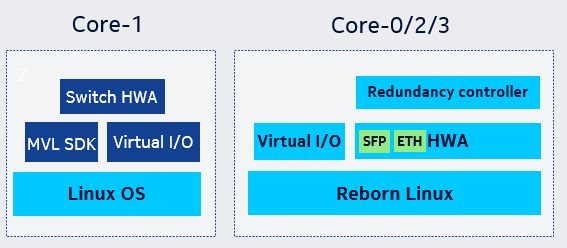
3. Common Linux
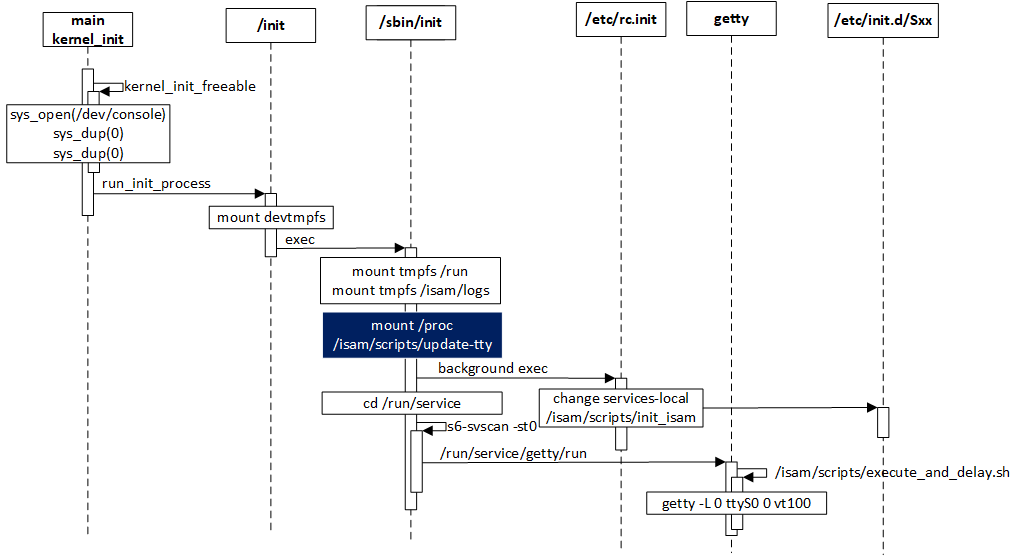
core0 和 core1 的 Linux 可以使用相同的 kernel config(需增加kernel配置CONFIG_MAPPED_KERNEL=y),相同的 driver 库,不同的地方是 tty 名称和启动脚本,所以我们在启动中识别 coreid 来更新 tty 名称和调用对应的启动脚本,如下图所示。
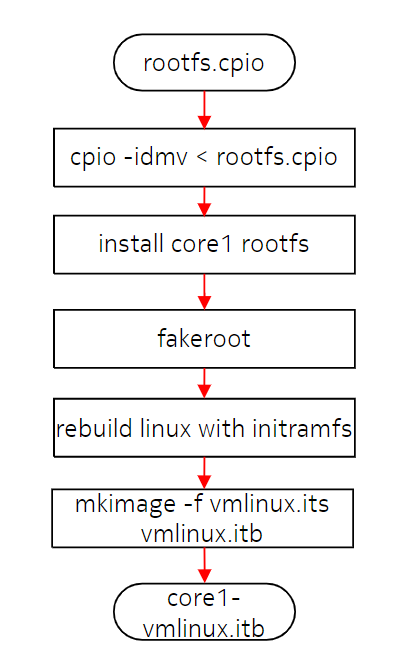
3.1 Core-1 Linux 编译
core0 和 core1 Linux image 的 rootfs 不完全相同,在 core0 rootfs 基础上经过二次编译得到(解压 core0 rootfs.cpio, 修改 rootfs,然后重新编译 Linux initramfs),流程如下:
4. core-1 Linux OS 启动
由 application 和 remoteproc drver 组成,框图如下:
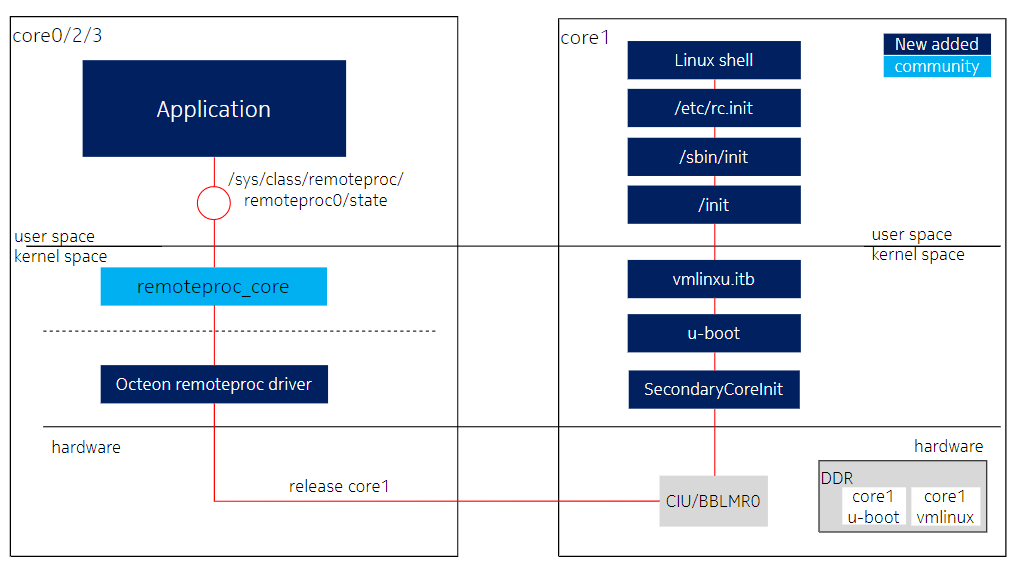
application 负责 启动 core1 并监控 core1 状态: (1)通过写 remoteroc driver 导出的 sysfs文件 kickoff core1; (2)通过 hwwd/reset 驱动创建的 uio 设备监控 core1 wathdog/reset 中断:如果一段时间没有收到 watchdog 中断,或者收到 reset 中断,将重启板卡。
remoteproc driver 实现 kickoff core1。
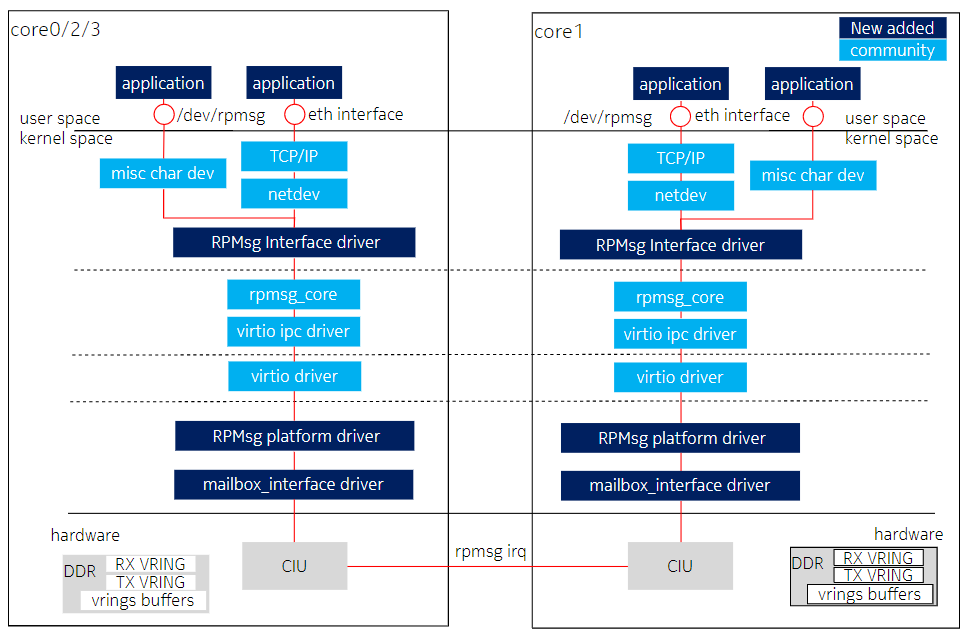
5. core0 和 core1 通信
rpmsg/virtio driver实现core0和core1之间的通信功能,框图如下:
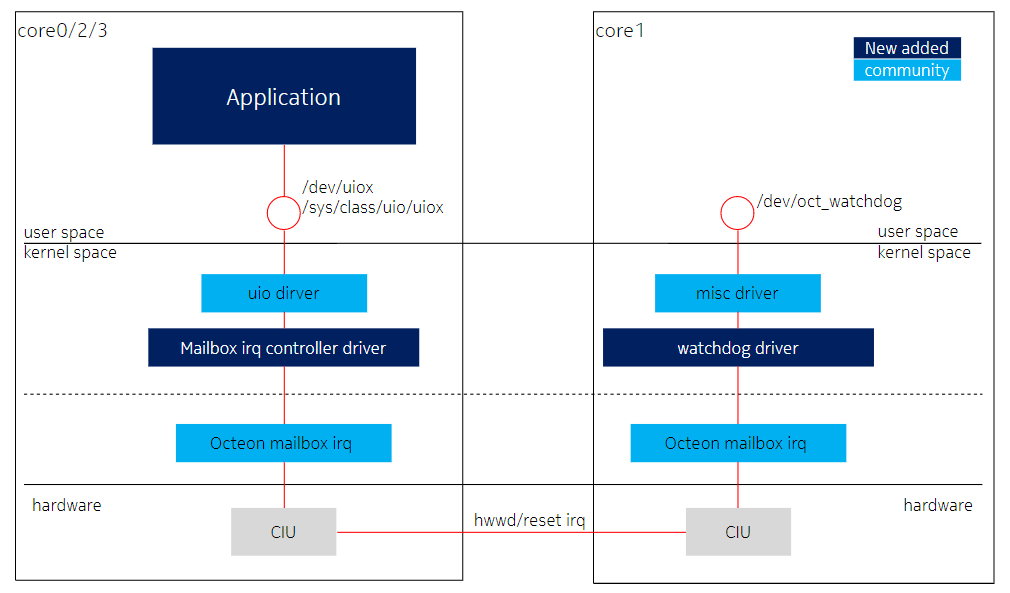
6. hwwd/reset/watchdog driver
core0 实现 mailbox irq controller 和 uio irq driver 接收 core1 的 hardware watchdog 和 reset 中断;core1 实现 watchdog driver 向 core0 发送 watchdog 中断。